
实现多模态 RAG 系统
作者 | Ideogram 提供图片
大型语言模型(LLM)的演变以及它们渗透到我们生活中的速度之快,以至于在各种场景下,我们都越来越依赖它们。当人们意识到像 ChatGPT 这样的文本生成产品如此有帮助时,很少有人能避免依赖它们。然而,有时答案是不准确的,这促使需要像检索增强生成(RAG)这样的输出增强技术。
RAG 是一个框架,通过整合外部知识的实时检索来增强 LLM 的输出。多模态 RAG 系统更进一步,能够跨越文本和图像数据等多种数据格式进行信息检索和处理。
在本文中,我们将使用文本、音频和图像数据来实现多模态 RAG。
多模态 RAG 系统
多模态 RAG 系统通过访问我们的知识库,利用多种数据集类型来实现更好的输出。实现它们的方式有很多种,但重要的是创建一个在生产环境中表现良好的系统,而不是一个花哨的系统。
在本教程中,我们将通过构建包含图像和音频数据的知识库来增强 RAG 系统。您可以在以下 GitHub 仓库 中找到完整的代码库。
工作流程可以用下图总结。
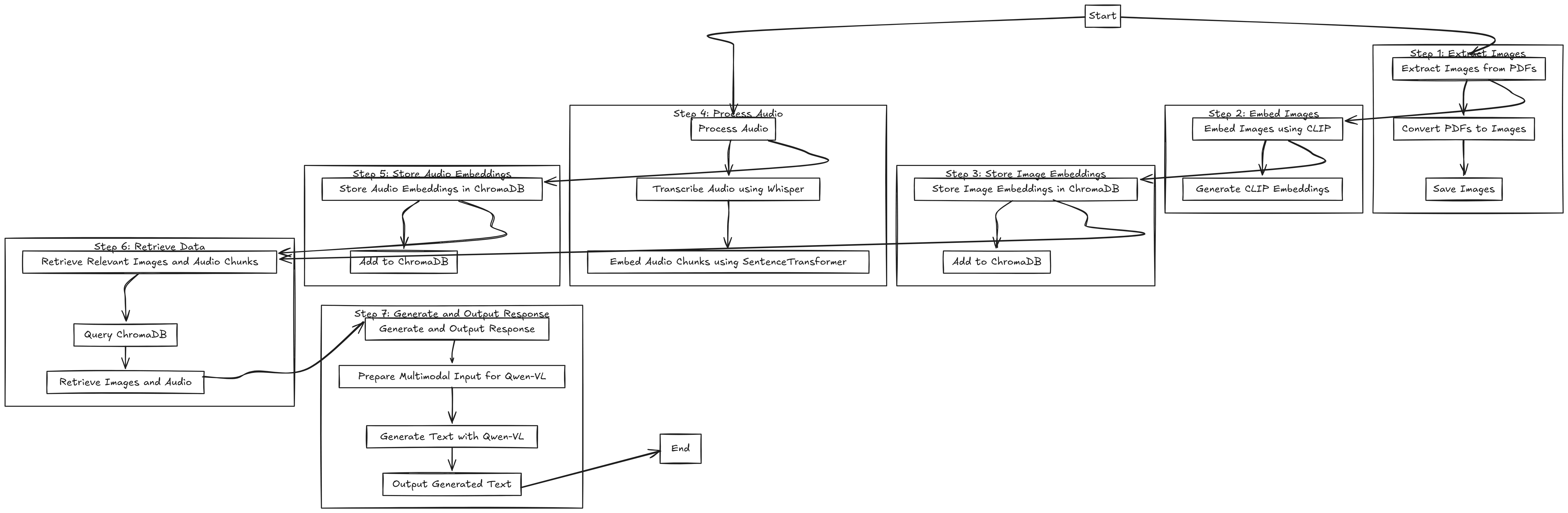
多模态 RAG 系统工作流程实现摘要(点击放大)
它现在有点小,看不清楚,所以请点击放大或按需保存并放大。工作流程可总结为七个步骤,即
- 提取图像
- 嵌入图像
- 存储图像嵌入
- 处理音频
- 存储音频嵌入
- 检索数据
- 生成并输出响应
由于这需要高资源,我们将使用 Google Colab 并访问 GPU。更具体地说,我们将使用 A100 GPU,因为本教程的 RAM 要求相对较高。
让我们开始安装我们教程中所有重要的库。
|
1 |
pip install pdf2image Pillow chromadb torch torchvision torchaudio transformers librosa ipython open-clip-torch qwen_vl_utils |
您可以访问 PyTorch 网站,了解哪一个适合您的系统和环境。
另外,有时从 PDF 提取图像可能无法正常工作。如果发生这种情况,您应该安装以下工具。
|
1 2 |
apt-get update apt-get install -y poppler-utils |
准备好环境和工具后,我们将导入所有必要的库。
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 |
import os from pdf2image import convert_from_path from PIL import Image import chromadb from chromadb.utils.embedding_functions import OpenCLIPEmbeddingFunction import torch from transformers import CLIPProcessor, CLIPModel, WhisperProcessor, WhisperForConditionalGeneration, Qwen2VLForConditionalGeneration, Qwen2VLProcessor import librosa from sentence_transformers import SentenceTransformer from qwen_vl_utils import process_vision_info from IPython.display import display, Image as IPImage |
在本教程中,我们将使用 PDF 中的图像数据以及之前准备好的音频文件(.mp3)。我们将使用 联合利华的简短烹饪食谱 作为 PDF 文件,以及 戈登·拉姆齐烹饪音频 文件来自 YouTube。您可以在 GitHub 仓库的 dataset 文件夹中找到这两个文件。
将所有文件放入 dataset 文件夹,我们就可以开始了。
我们将首先处理 PDF 文件中的图像数据。为此,我们将使用以下代码将 PDF 的每一页提取为图像。
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 |
output_dir = "dataset" image_output_dir = "extracted_images" def convert_pdfs_to_images(folder, image_output_dir): if not os.path.exists(image_output_dir): os.makedirs(image_output_dir) pdf_files = [f for f in os.listdir(folder) if f.endswith('.pdf')] all_images = {} for doc_id, pdf_file in enumerate(pdf_files): pdf_path = os.path.join(folder, pdf_file) images = convert_from_path(pdf_path, dpi=100) image_paths = [] for i, image in enumerate(images): image_path = os.path.join(image_output_dir, f"{doc_id}_page_{i}.png") image.save(image_path, "PNG") image_paths.append(image_path) all_images[doc_id] = image_paths return all_images all_images = convert_pdfs_to_images(output_dir, image_output_dir) |
从 PDF 文件中提取所有图像后,我们将使用 CLIP 模型 生成图像嵌入。CLIP 是 OpenAI 开发的多模态模型,旨在理解图像和文本数据之间的关系。
在我们的流程中,我们使用 CLIP 生成图像嵌入,稍后将其存储在 ChromaDB 向量数据库中,并根据文本查询检索相关图像。
要生成图像嵌入,我们将使用以下代码。
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 |
device = "cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu" model = CLIPModel.from_pretrained("openai/clip-vit-base-patch32").to(device) processor = CLIPProcessor.from_pretrained("openai/clip-vit-base-patch32") def embed_images(image_paths): embeddings = [] for path in image_paths: image = Image.open(path) inputs = processor(images=image, return_tensors="pt", padding=True).to(device) with torch.no_grad(): image_embedding = model.get_image_features(**inputs).cpu().numpy() embeddings.append(image_embedding) return embeddings image_embeddings = {} for doc_id, paths in all_images.items(): image_embeddings[doc_id] = embed_images(paths) |
接下来,我们将使用 Whisper 模型 处理音频数据以生成文本转录。Whisper 是一个 OpenAI 模型,它使用基于 Transformer 的架构从音频输入生成文本。
我们在流程中不使用 Whisper 进行嵌入。相反,它将仅负责音频转录。我们将分块转录音频,然后使用 sentence transformers 为转录块生成嵌入。
为了处理音频转录,我们将使用以下代码。
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 |
whisper_processor = WhisperProcessor.from_pretrained("openai/whisper-small") whisper_model = WhisperForConditionalGeneration.from_pretrained("openai/whisper-small").to(device) # 定义每段文本的长度 def transcribe_audio(audio_path, chunk_length=30): audio, sr = librosa.load(audio_path, sr=16000) chunk_size = chunk_length * sr chunks = [audio[i:i + chunk_size] for i in range(0, len(audio), chunk_size)] transcription_chunks = [] for chunk in chunks: inputs = whisper_processor(chunk, sampling_rate=sr, return_tensors="pt").to(device) inputs["attention_mask"] = torch.ones_like(inputs.input_features) with torch.no_grad(): predicted_ids = whisper_model.generate(**inputs, max_length=448) chunk_transcription = whisper_processor.batch_decode(predicted_ids, skip_special_tokens=True)[0] transcription_chunks.append(chunk_transcription) full_transcription = " ".join(transcription_chunks) return full_transcription, transcription_chunks audio_files = [f for f in os.listdir(output_dir) if f.endswith('.mp3')] audio_transcriptions = {} for audio_id, audio_file in enumerate(audio_files): audio_path = os.path.join(output_dir, audio_file) full_transcription, transcription_chunks = transcribe_audio(audio_path) audio_transcriptions[audio_id] = { "full_transcription": full_transcription, "chunks": transcription_chunks } |
一切就绪后,我们将把嵌入存储在 ChromaDB 向量数据库中。我们将分离图像和音频转录数据,因为它们的嵌入特征不同。我们还将初始化图像和音频转录数据的嵌入函数。
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 |
client = chromadb.PersistentClient(path="chroma_db") embedding_function = OpenCLIPEmbeddingFunction() text_embedding_model = SentenceTransformer('sentence-transformers/all-MiniLM-L6-v2') # 删除现有集合(如果需要) try: client.delete_collection(name="image_collection") client.delete_collection(name="audio_collection") print("Deleted existing collections.") except Exception as e: print(f"Collections do not exist or could not be deleted: {e}") image_collection = client.create_collection(name="image_collection", embedding_function=embedding_function) audio_collection = client.create_collection(name="audio_collection") for doc_id, embeddings in image_embeddings.items(): for i, embedding in enumerate(embeddings): image_collection.add( ids=[f"image_{doc_id}_{i}"], embeddings=[embedding.flatten().tolist()], metadatas=[{"doc_id": str(doc_id), "image_path": all_images[doc_id][i]}] ) for audio_id, transcription_data in audio_transcriptions.items(): transcription_chunks = transcription_data["chunks"] for chunk_id, chunk in enumerate(transcription_chunks): chunk_embedding = text_embedding_model.encode(chunk) audio_collection.add( ids=[f"audio_{audio_id}_chunk_{chunk_id}"], embeddings=[chunk_embedding.tolist()], metadatas=[{ "audio_id": str(audio_id), "audio_path": audio_files[audio_id], "chunk_id": str(chunk_id) }], documents=[chunk] ) |
我们的RAG系统几乎准备就绪!唯一剩下要做的就是从ChromaDB向量数据库设置检索系统。
例如,让我们尝试使用文本查询从图像和音频文件中检索前两个结果。
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 |
def retrieve_data(query, top_k=2): query_embedding_image = embedding_function([query])[0] # OpenCLIP 用于图像集合 query_embedding_audio = text_embedding_model.encode(query) # SentenceTransformer 用于音频集合 image_results = image_collection.query( query_embeddings=[query_embedding_image], n_results=top_k ) audio_results = audio_collection.query( query_embeddings=[query_embedding_audio.tolist()], n_results=top_k ) retrieved_images = [metadata["image_path"] for metadata in image_results["metadatas"][0] if "image_path" in metadata] retrieved_chunks = audio_results["documents"][0] if "documents" in audio_results else [] return retrieved_images, retrieved_chunks query = "What are the healthiest ingredients to use in the recipe you have?" retrieved_images, retrieved_chunks = retrieve_data(query) print("Retrieved Images:", retrieved_images) print("Retrieved Audio Chunks:", retrieved_chunks) |
检索结果如下面的输出所示。
|
1 2 3 |
Retrieved Images: ['extracted_images/0_page_3.png', 'extracted_images/0_page_12.png'] Retrieved Audio Chunks: [" Lemon. Zest the lemon. Over. Smells incredible. And then finally seal the deal with a touch of grated parmesan cheese. Give your veg some attitude and you'll get amazingly elegant dishes on a budget that are always guaranteed to impress. What more do you want from great cooking? Cheap to make, easy to cook and absolutely stunning. For me, food always has to be impressive. But when it comes to desserts,", " and one third of your protein, chicken. With a dish that takes literally minutes to put together, it's really important to get everything organized. Everything needs to be at your fingertips. Touch of olive oil. Get that pan really nice and ready. Just starting to smoke. Drop the chicken in first. Just salt, pepper. Open up those little strands of chicken."] |
对于图像检索,它将返回我们在向量数据库中存储的元数据图像路径。对于音频检索,它返回与文本查询最相关的转录块。
通过数据检索,我们将使用 Qwen-VL 模型 设置生成模型。该模型是一个多模态 LLM,可以处理文本和图像数据,并从我们传入的多模态数据生成文本响应。
我们使用 Qwen-VL 模型,它通过同时接受检索到的图像和音频转录块来生成多模态文本响应。
让我们用以下代码设置模型。
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 |
vl_model = Qwen2VLForConditionalGeneration.from_pretrained( "Qwen/Qwen2-VL-7B-Instruct", torch_dtype=torch.bfloat16, ).cuda().eval() min_pixels = 256 * 256 max_pixels = 1024 * 1024 vl_model_processor = Qwen2VLProcessor.from_pretrained( "Qwen/Qwen2-VL-7B-Instruct", min_pixels=min_pixels, max_pixels=max_pixels ) |
然后,我们设置模型以接受输入数据、处理它们并生成文本输出。
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 |
chat_template = [ { "role": "user", "content": [ {"type": "image", "image": retrieved_images[0]}, # 第一张检索到的图片 {"type": "image", "image": retrieved_images[1]}, # 第二张检索到的图片 {"type": "text", "text": query}, # 用户查询 {"type": "text", "text": "Audio Context: " + " ".join(retrieved_chunks)} # 包含音频数据 ], } ] text = vl_model_processor.apply_chat_template( chat_template, tokenize=False, add_generation_prompt=True ) image_inputs, _ = process_vision_info(chat_template) inputs = vl_model_processor( text=[text], images=image_inputs, padding=True, return_tensors="pt", ).to("cuda") generated_ids = vl_model.generate(**inputs, max_new_tokens=100) generated_ids_trimmed = [ out_ids[len(in_ids):] for in_ids, out_ids in zip(inputs.input_ids, generated_ids) ] output_text = vl_model_processor.batch_decode( generated_ids_trimmed, skip_special_tokens=True, clean_up_tokenization_spaces=False ) print(output_text[0]) |
结果如下面的输出所示。
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 |
The healthiest ingredients to use in the recipe are: 1. **Lemon** - Provides a burst of citrus flavor and is a good source of vitamin C. 2. **Parmesan Cheese** - A good source of calcium and protein. 3. **Chicken** - A lean protein source that is rich in essential amino acids. 4. **Olive Oil** - A healthy fat that is rich in monounsaturated fatty acids. 5. **Zest** - Adds a burst of flavor |
正如你所见,结果同时考虑了图像和音频数据。
这就是构建多模态 RAG 系统所需的所有内容。您可以根据需要更改文件和代码。
结论
检索增强生成(Retrieval-Augmented Generation,RAG)是一种利用外部知识来增强 LLM 输出的框架。在多模态 RAG 系统中,我们利用文本以外的数据,例如图像和音频数据。
在本文中,我们使用文本、音频和图像数据实现了多模态 RAG。我们使用 CLIP 进行图像嵌入,使用 Whisper 进行音频转录,使用 SentenceTransformer 进行文本嵌入,使用 ChromaDB 进行向量存储,以及使用 Qwen-VL 进行多模态文本生成。
希望这对您有所帮助!




暂无评论。